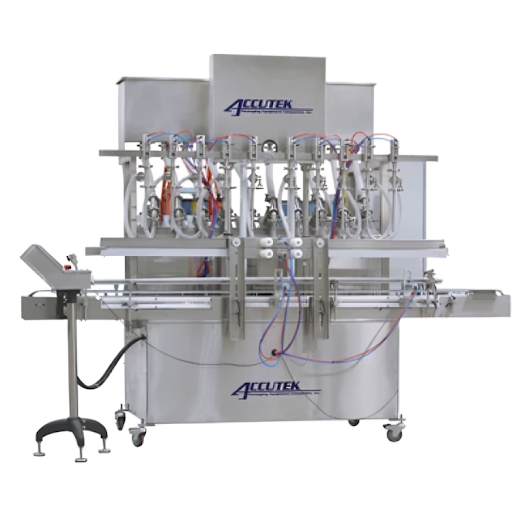
Have you ever noticed how your favorite bottled beverages, pharmaceuticals, or personal care products are packed into perfectly filled containers in the exact same quantity?
Manually, it’s difficult to fill liquids into containers precisely and efficiently in a large amount.
You must be curious to know the answer! It all happens because of automated liquid-filling machines specially designed and used to fill liquid products.
If you want to learn the whole process from beginning to end, this blog is for you.
Liquid product filling is a crucial process in various industries, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and household chemicals. The efficiency and accuracy of this process directly impact product quality, safety, and consumer satisfaction.
The automatic filling machine is most important in optimizing these factors, enabling manufacturers to meet high standards and regulatory requirements while maximizing production efficiency.
The need for greater precision, speed, and adaptability has driven the evolution of filling equipment.
With sophisticated technologies, advanced liquid filling machines optimize packaging efficiency through various liquids for seamless operation, minimal waste, and rapid changeovers.
Let’s examine the fundamentals of liquid product filling and the components of these advanced systems.
Fundamentals of Liquid Product Filling
Liquid products come in various forms, from thin, free-flowing liquids like water and juice to viscous substances like syrups and lotions. Each type of liquid presents unique challenges in terms of filling and packaging.
That’s why understanding the properties of the liquid is essential for selecting the appropriate filling method and equipment.
The two primary methods of liquid filling are ‘Volumetric’ and ‘Gravimetric.’
- Volumetric Filling
Volumetric filling measures the volume of liquid dispensed into each container, ensuring consistent fill levels. Because of its precise volume control, volumetric filling equipment is used in diverse industries.
- Gravimetric Filling
Gravimetric filling on the other hand, measures the weight of the liquid, providing high accuracy and consistency, especially for viscous (gluey) or foamy products.
Multiple factors influence the accuracy and efficiency of liquid filling, including the product’s viscosity, the type of container, and the filling speed.
Liquid filling machines are designed to accommodate these variables, offering adjustable settings and specialized components to handle different products and packaging requirements.
Types of Advanced Filling Equipment
Automatic filling machines come in various types, each suited to specific applications and product characteristics.
Some of the most common types include:
- Piston Fillers
Piston fillers use a piston mechanism to draw liquid into a cylinder and dispense it into containers. They are ideal for thick, viscous products and provide precise volume control.
- Rotary Fillers
Rotary fillers are designed for high-speed operations and can handle various liquid viscosities. They use a rotating filling head that moves containers in a circular motion, ensuring efficient and continuous filling.
- Vacuum Fillers
Vacuum fillers use vacuum pressure to draw liquid into containers. They are particularly effective for filling low-viscosity liquids and can handle products prone to foaming.
- Time-Pressure Fillers
Time-pressure fillers use time and pressure to control the amount of liquid dispensed. They are versatile and can be used for a variety of liquid products.
Key Components and Their Roles
Automatic filling machines comprise several key components, each playing a crucial role in the filling process.
- Filling Nozzles
The filling nozzles dispensing the liquid into containers are designed to minimize splashing, foaming, and dripping, ensuring a clean and accurate fill.
- Control Systems
Modern liquid filling machines have sophisticated control systems that allow operators to adjust settings, monitor performance, and troubleshoot issues. These systems often include touchscreens, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and sensors for real-time feedback.
- Conveyors and Platforms
Conveyors and platforms facilitate the movement of containers through the filling line. They ensure smooth and continuous operation, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency.
Step-by-Step Process through Advanced Filling Equipment
The journey of liquid products through advanced filling equipment involves several stages, each critical to achieving a high-quality fill.
Product Preparation and Feeding
Before the filling process begins, the liquid product must be properly prepared and fed into the filling machine. This may involve mixing, heating, or degassing the product to ensure consistency and prevent issues during filling. The product is pumped or gravity-fed into the machine’s reservoir or hopper.
Container Handling and Preparation
Containers are fed into the filling line via a conveyor system. Automatic filling machines have mechanisms to orient, space, and stabilize containers, ensuring they are correctly positioned for filling.
Some systems also include rinsing or sterilizing units to clean containers before filling.
Filling Process Stages
Filling Process Stages encompass a series of well-defined steps to ensure the accurate and efficient filling of containers.
Let’s discuss these stages in detail one by one.
- Initial Setup and Calibration
The filling machine is calibrated to ensure accurate fill levels. This involves setting parameters such as volume filling, speed, and pressure based on the product and container specifications.
- Actual Filling Operation
The filling nozzles dispense the liquid into the containers. Advanced machines use sensors and feedback systems to monitor the filling levels and make real-time adjustments, ensuring precision and consistency.
- Monitoring and Adjustment
Throughout the filling process, the machine continuously monitors performance. Any deviations from the set parameters are automatically corrected, minimizing waste and ensuring uniform fills.
- Post-Filling Procedures
After dispensing the liquid, the containers are moved to post-filling stations, sealed, capped, or closed.
Capping
Capping is a vital step in the post-filling process. It involves securing a cap or lid onto the filled container to protect the product from contamination, leakage, and spoilage. There are several types of capping machines, each designed for different kinds of closures:
- Snap Cappers
- Screw Cappers
- Crimp Cappers
Labeling
Labeling is the final step in the post-filling process. It involves applying labels to the containers and providing crucial information such as product name, trademark, essential ingredients, usage instructions, batch numbers, expiry dates, barcodes, etc. Accurate labeling is vital for regulatory compliance and consumer information.
There are various types of labeling machines, each suited to different container shapes and sizes:
- Wrap-Around Labelers
- Front-and-Back Labelers
- Top-and-Bottom Labelers
Conclusion
From understanding the intricate process of liquid filling and the role of liquid filling machines, you now know how delicate the manufacturing and packaging industry is.
It highlights the critical interplay between technology and production, ensuring that liquid products reach consumers best.
As we look ahead, the journey of liquid products through advanced filling equipment will continue to be a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.